Introduction
Managing your web hosting account doesn’t have to be intimidating. If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by the technical aspects of website management, cPanel is your friendly gateway to taking control of your hosting environment. This powerful control panel transforms complex server management tasks into simple point-and-click operations that anyone can master.
Whether you’re a complete beginner who just purchased your first hosting account or an experienced user looking to maximize cPanel’s capabilities, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know. We’ll cover the essentials first, then dive into advanced features that can help you optimize your website’s performance and security.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be confidently managing domains, email accounts, databases, and security settings like a pro, without needing to touch a single line of code.
Getting Started with cPanel
Accessing Your cPanel Account
Finding Your cPanel Login: Most hosting providers send you cPanel login credentials immediately after purchasing hosting. Look for an email with the subject line containing “Welcome” or “Account Information.” Your cPanel URL typically follows one of these formats:
- yourdomain.com/cpanel
- yourdomain.com:2083
- server.hostingprovider.com/cpanel
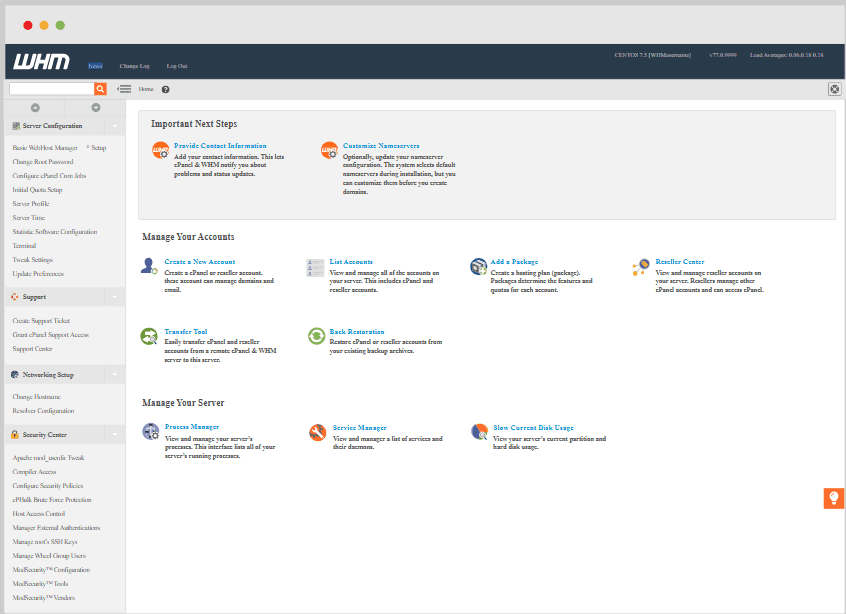
First Login Experience: When you first log into cPanel, you’ll see a dashboard filled with colorful icons representing different functions. Don’t worry if it seems overwhelming; we’ll break down each section systematically. The interface is designed to be intuitive, with related functions grouped in logical categories.
Understanding the Dashboard Layout: cPanel organizes tools into categories like Files, Databases, Email, Metrics, Security, and Software. Each category contains related functions, making it easy to find what you need once you understand the basic structure.
Essential cPanel Navigation
The Search Function: One of cPanel’s most underutilized features is the search bar at the top of the interface. Instead of hunting through categories, simply type what you’re looking for, like “email,” “backup,” or “file manager,” and cPanel will highlight relevant tools.
Customizing Your View: You can customize your cPanel dashboard by changing the theme, rearranging icons, or switching between different view modes. Many users prefer the “Paper Lantern” theme for its clean, modern appearance and logical organization.
Quick Access Shortcuts: cPanel remembers your most frequently used tools and can display them prominently on your dashboard. This personalization makes daily management tasks much more efficient.
File Management Made Simple
Using File Manager Effectively
Navigating Your Website Files: File Manager is like Windows Explorer or Mac Finder for your website. Your main website files live in the “public_html” folder (or “www” on some servers). This is where you’ll upload your website files, images, and other content that visitors can access.
Essential File Operations
- Uploading Files: Drag and drop files directly into File Manager or use the upload button for larger files
- Creating Folders: Right-click in any directory to create new folders for organizing content
- Editing Files: Double-click text files to edit them directly in cPanel’s built-in editor
- Setting Permissions: Right-click files to adjust permissions for security and functionality
File Manager Best Practices: Always create backups before making significant changes to your files. Use descriptive folder names and maintain a logical structure that will make sense to you months later. Keep your file sizes optimized, as large images and videos can slow down your website significantly.
Understanding File Permissions
Permission Basics: File permissions control who can read, write, or execute files on your server. The three-digit permission system (like 644 or 755) might seem confusing, but understanding the basics helps maintain security.
Common Permission Settings:
- 644: Standard for most files (owner can read/write, others can only read)
- 755: Standard for directories and executable files
- 777: Full permissions (use sparingly and only when necessary)
Security Considerations: Never set permissions to 777 unless necessary, as this makes files writable by everyone and creates security vulnerabilities. When in doubt, stick with 644 for files and 755 for folders.
Domain and Subdomain Management
Managing Multiple Domains
Adding New Domains: If your hosting plan supports multiple domains, you can add them through the “Addon Domains” section. Each addon domain gets its own folder within your hosting account, allowing you to host completely separate websites.
Understanding Domain Types
- Main Domain: Your primary domain associated with the hosting account
- Addon Domains: Additional domains with separate websites
- Subdomains: Extensions of your main domain (like blog.yourdomain.com)
- Parked Domains: Alternative domains that display the same content as your main site
Domain Redirection: Use the “Redirects” feature to automatically forward visitors from one domain or page to another. This is particularly useful when changing domain names or restructuring your website.
Creating and Managing Subdomains
When to Use Subdomains: Subdomains work well for creating distinct sections of your website with different purposes:
- blog.yourdomain.com for your company blog
- shop.yourdomain.com for e-commerce
- support.yourdomain.com for customer service
Setting Up Subdomains: Navigate to “Subdomains” in cPanel, enter your desired subdomain name, and cPanel automatically creates the necessary folder structure. You can then upload content specific to that subdomain.
Subdomain Best Practices: Keep subdomain names short, descriptive, and relevant to their content. Consider how subdomains affect your SEO strategy, as search engines treat them as separate entities from your main domain.
Email Account Administration
Creating Professional Email Accounts
Setting Up Email Accounts: Professional email addresses using your domain name (like [email protected]) look more credible than free email services. Navigate to “Email Accounts” to create new addresses, set passwords, and configure storage quotas.
Email Storage Management: Monitor email storage usage regularly to prevent accounts from becoming full and bouncing incoming messages. Set appropriate quotas based on each user’s needs. Executives might need more storage than occasional users.
Email Security Settings: Enable spam filters and antivirus scanning to protect your email accounts from threats. Configure these settings conservatively at first, then adjust based on your experience with false positives.
Advanced Email Features
Email Forwarders: Create email forwarders to automatically redirect messages from one address to another. This feature is useful for creating alias addresses (like [email protected] forwarding to [email protected]) or temporarily redirecting email during staff changes.
Autoresponders: Set up autoresponders for situations like vacation messages, acknowledgment emails, or providing automatic information to common inquiries. Keep autoresponder messages professional and include alternative contact methods when appropriate.
Mailing Lists: For businesses that send regular newsletters or updates, cPanel’s mailing list feature provides basic bulk email capabilities. However, for professional email marketing, consider dedicated services like Mailchimp or ConvertKit.
Email Client Configuration
IMAP vs POP3: Choose IMAP for email access from multiple devices, as it keeps messages synchronized across all your devices. Use POP3 only if you primarily check email from a single computer and want to download messages locally.
Security Settings: Always use encrypted connections (SSL/TLS) when configuring email clients. cPanel provides the exact settings you need for popular email programs like Outlook, Apple Mail, and mobile devices.
Troubleshooting Email Issues: Common email problems include incorrect server settings, full mailboxes, and spam filter blocks. cPanel’s email troubleshooting tools can help diagnose connection issues and delivery problems.
Database Management Essentials
Understanding MySQL Databases
What Databases Do: Databases store dynamic content for your website, including user accounts, blog posts, product information, and configuration settings. Most modern websites and applications require database functionality.
Creating Databases: Use “MySQL Databases” to create new databases for your applications. Choose descriptive names that will make sense later. You might have separate databases for your main website, blog, and customer portal.
Database Users and Privileges: Create specific database users with limited privileges for security. Don’t use your main cPanel credentials for database connections in your applications. Instead, create dedicated users with only the permissions they need.
phpMyAdmin for Advanced Users
Accessing phpMyAdmin: phpMyAdmin provides a web-based interface for advanced database management. Use it for tasks like importing/exporting data, running SQL queries, and optimizing database performance.
Common phpMyAdmin Tasks
- Importing database backups from other servers
- Exporting data for backups or migrations
- Running SQL queries for bulk data changes
- Optimizing tables for better performance
Safety Precautions: Always backup your database before making changes in phpMyAdmin. Incorrect modifications can break your website or cause data loss. When in doubt, consult with your hosting provider’s support team.
Security and Backup Management
Essential Security Features
Password Protection: Use cPanel’s “Password Protect Directories” feature to add an extra layer of security to sensitive areas of your website. This creates HTTP authentication that requires a username and password before accessing protected content.
IP Blocking: The “IP Blocker” tool allows you to block specific IP addresses or ranges from accessing your website. Use this feature to block persistent attackers or unwanted traffic sources.
Hotlink Protection: Enable hotlink protection to prevent other websites from directly linking to your images and files, which can consume your bandwidth and server resources without providing any benefit to your site.
Backup Strategies
Automated Backups: Many hosting providers offer automated backup services, but you can also create manual backups through cPanel’s backup feature. Regular backups are essential insurance against data loss, security breaches, or server failures.
Full vs Partial Backups
- Full Backups: Complete copies of your entire hosting account, including files, databases, and email
- Partial Backups: Selective backups of specific elements like databases or particular directories
Backup Storage: Store backup copies in multiple locations, like on your local computer, cloud storage services, or with backup service providers. Don’t rely solely on your hosting provider’s backup systems.
SSL Certificate Management
Understanding SSL Certificates: SSL certificates encrypt data transmission between your website and visitors, essential for security and search engine rankings. Modern browsers display security warnings for websites without SSL certificates.
Installing SSL Certificates: Many hosting providers offer free SSL certificates through Let’s Encrypt integration in cPanel. Navigate to “SSL/TLS” to install, manage, or renew certificates for your domains.
SSL Troubleshooting: Common SSL issues include mixed content warnings (loading non-HTTPS resources on HTTPS pages) and certificate mismatches. cPanel’s SSL tools can help diagnose and resolve these problems.
Performance Optimization Tools
Caching and Compression
Understanding Caching: Caching stores frequently accessed data in quickly retrievable formats, reducing server load and improving page loading speeds. cPanel often includes caching tools or integrates with caching plugins.
File Compression: Enable GZIP compression to reduce the size of files transmitted to visitors’ browsers. This simple optimization can significantly improve loading speeds, especially for users on slower connections.
Image Optimization: Large images are often the biggest culprit in slow website performance. Use cPanel’s file management tools to organize and optimize images, or integrate with image optimization services.
Resource Monitoring
Disk Space Usage: Monitor your disk space usage regularly to avoid reaching account limits. Use cPanel’s disk usage tools to identify large files or directories that might be consuming excessive space.
Bandwidth Monitoring: Track your bandwidth usage to understand traffic patterns and ensure you’re not approaching your hosting plan limits. Sudden bandwidth spikes might indicate security issues or viral content.
Error Log Analysis: Review error logs regularly to identify and resolve website issues before they affect visitors. Common errors include broken links, permission problems, and script failures.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Website Loading Problems
Identifying Performance Issues: Use cPanel’s error logs and statistics tools to diagnose slow loading times. Common causes include large file sizes, database inefficiencies, and resource limitations.
File Permission Problems: Incorrect file permissions can cause various website errors. Use File Manager to check and correct permissions, remembering that most files should be set to 644 and directories to 755.
Database Connection Errors: Database connection problems often stem from incorrect credentials, full databases, or server overload. Check your database settings and contact support if problems persist.
Email Delivery Issues
Spam Filter Problems: If legitimate emails aren’t reaching their destination, check spam filter settings and consider adjusting sensitivity levels. Sometimes, overly aggressive filtering blocks important messages.
Storage Quota Issues: Full email accounts stop receiving new messages. Regularly clean up old emails or increase storage quotas for high-volume users.
Authentication Problems: Email client configuration errors are common. Double-check server settings, ports, and encryption options using cPanel’s configuration guides.
Advanced cPanel Features
Cron Jobs for Automation
Understanding Cron Jobs: Cron jobs automatically execute scripts or commands at scheduled intervals. Use them for tasks like database backups, sending recurring emails, or updating website content.
Common Cron Job Applications
- Daily database backups
- Weekly security scans
- Monthly traffic report generation
- Automated content publishing
Setting Up Cron Jobs: Navigate to “Cron Jobs” in cPanel to create scheduled tasks. Be cautious with frequency settings, too many cron jobs can overload your server.
Custom Error Pages
Creating Professional Error Pages: Custom 404 and other error pages maintain your brand consistency even when visitors encounter problems. Use these pages to guide users back to relevant content rather than displaying generic error messages.
Error Page Best Practices: Include navigation links, search functionality, and helpful suggestions on custom error pages. Monitor which pages generate the most 404 errors and address broken links promptly.
Development Tools
Staging Environments: Some cPanel installations include staging environment tools that let you test changes before applying them to your live website. This feature is invaluable for maintaining website stability.
Version Control: Advanced users can integrate version control systems like Git through cPanel’s development tools. This allows professional development workflows and easy rollbacks when needed.
Getting Help and Support
Using cPanel Documentation
Built-in Help System: cPanel includes extensive help documentation accessible through question mark icons throughout the interface. This context-sensitive help provides specific guidance for each feature.
Video Tutorials: Many hosting providers offer video tutorials specifically for their cPanel implementation. These visual guides can be more helpful than written documentation for complex procedures.
When to Contact Support
Identifying Support-Worthy Issues: Contact your hosting provider’s support team for server-related problems, security issues, or when cPanel features aren’t working as expected. They can also help with advanced configurations beyond basic cPanel functionality.
Preparing for Support Contacts: Before contacting support, gather relevant information like error messages, screenshots, and steps you’ve already attempted. This helps support staff diagnose and resolve issues more quickly.
Best Practices for Long-term Success
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Weekly Maintenance
- Review error logs for new issues
- Check disk space and bandwidth usage
- Verify backup completion
- Monitor email account storage
Monthly Maintenance
- Update passwords for enhanced security
- Review and clean up unused files
- Analyze traffic patterns and performance
- Check for software updates
Quarterly Maintenance
- Comprehensive security audit
- Database optimization and cleanup
- Review and update backup strategies
- Evaluate the hosting plan adequacy
Security Hygiene
Password Management: Use strong, unique passwords for all cPanel and email accounts. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
Regular Updates: Keep all software, plugins, and applications updated to the latest versions. Many security vulnerabilities are fixed in updates, making regular maintenance crucial for security.
Access Control: Regularly review who has access to your cPanel account and email addresses. Remove access for former employees or contractors promptly.
Conclusion
Mastering cPanel empowers you to take full control of your web hosting environment without requiring extensive technical knowledge. From basic file management and email setup to advanced features like database administration and security configuration, cPanel provides the tools you need to maintain a professional web presence.
The key to cPanel success is starting with the basics and gradually exploring more advanced features as your needs grow. Don’t try to learn everything at once, focus on the functions you need immediately, then expand your knowledge over time.
Remember that cPanel is a powerful tool, and with power comes responsibility. Always backup your data before making significant changes, use strong security practices, and don’t hesitate to contact your hosting provider’s support team when you encounter issues beyond your comfort level.
With the knowledge gained from this guide, you’re well-equipped to manage your hosting account confidently and efficiently. cPanel transforms complex server management into manageable tasks, putting professional website administration within reach of anyone willing to learn.
Your website is a valuable business asset, and proper hosting management through cPanel helps ensure it remains secure, fast, and reliable for your visitors. Take the time to implement these best practices, and you’ll build a solid foundation for your online success.